Discovering the Nyala: Africa’s Hidden Gem
Discovering the Nyala: Africa’s Hidden Gem
Africa, a continent bursting with wildlife diversity, holds mysteries waiting to be unveiled. Amongst its vast landscapes and unique ecosystems, there lies a creature that epitomizes the beauty and complexity of African fauna – the Nyala. This antelope, lesser-known compared to its more famous counterparts like elephants and lions, is a true hidden gem. Native to Southern Africa, Nyalas are a testament to the continent’s rich biodiversity and the intricate ties that bind African wildlife to its environment.
The Enigmatic Nyala: A Closer Look
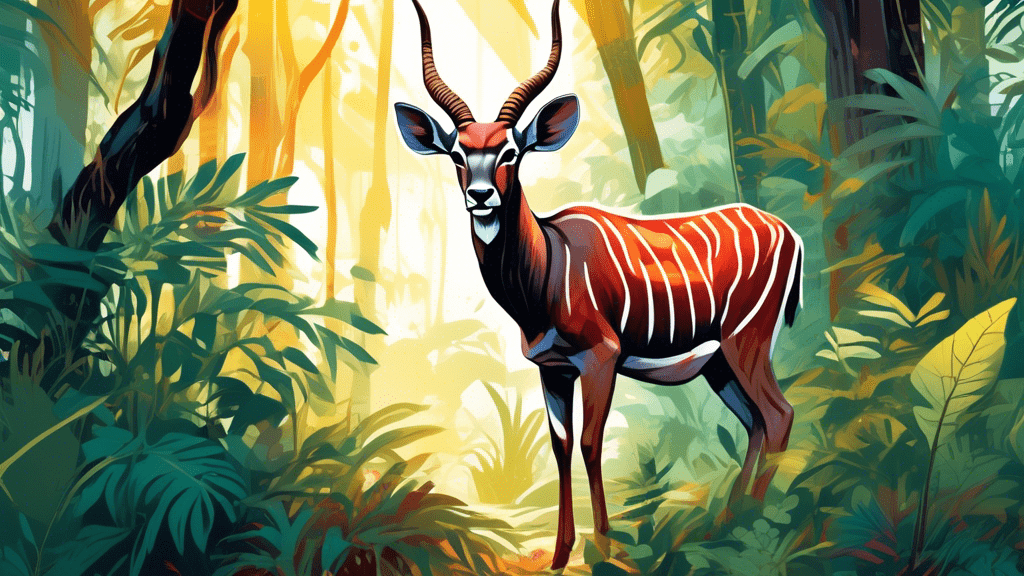
The Nyala (Tragelaphus angasii) stands out for its striking appearance. Males and females display a remarkable sexual dimorphism, making them one of the most interesting antelopes to observe. Males are significantly larger than females and are adorned with dark brown or slate-grey coats that contrast sharply with the females’ chestnut-colored fur. The males boast long, spiraled horns and a shaggy mane along their underside, from chin to tail, adding to their majestic appearance. In contrast, females and juveniles possess no horns and are characterized by their ten or more distinctive white stripes that run laterally across their bodies. This camouflage is key to their survival in the woodland and thickets they call home.
Habitat and Conservation
Nyalas are primarily found in the dense bushlands and lowland forests of southeastern Africa, with a concentration in countries such as South Africa, Mozambique, Malawi, and Zimbabwe. They are creatures of the shadows, preferring habitats that offer ample cover and access to water sources. This preference makes them elusive, adding a layer of mystique that often surrounds these beautiful antelopes.
Conservation efforts for Nyala populations have seen varying degrees of success over the years. While not currently listed as an endangered species, they are at risk from habitat loss due to human encroachment, deforestation, and the expanding agricultural frontier. Poaching has also posed a significant threat in certain areas. Consequently, conservation initiatives focusing on habitat restoration, anti-poaching campaigns, and community-based conservation strategies are crucial in ensuring the survival of this remarkable species.
Nyala in Culture and Economy
The Nyala holds a special place in African culture and heritage. In some regions, they are symbols of prosperity and wealth, often associated with traditional rituals and ceremonies. Their presence is a sign of a healthy and balanced ecosystem, reflecting the intimate relationship between the people and wildlife of Africa.
In addition to their cultural significance, Nyalas also contribute to Africa’s economy through eco-tourism and game reserves. Observing these majestic creatures in their natural habitat is a sought-after experience for wildlife enthusiasts and nature lovers from around the globe. Their allure attracts tourists, which in turn generates revenue that can be channeled back into conservation efforts and local community development.
Conclusion
The Nyala is indeed Africa’s hidden gem, embodying the continent’s wild heart and soul. Through understanding and appreciating these antelopes, we gain insight into the broader challenges and triumphs of wildlife conservation in Africa. It is a reminder of the delicate balance that exists within nature and the responsibility we carry to protect it. By shining a light on lesser-known species like the Nyala, we can foster a deeper connection to the natural world and inspire action toward its preservation.
FAQs: Discovering the Nyala
What distinguishes the Nyala from other African antelopes?
What sets the Nyala apart from other African antelopes is its pronounced sexual dimorphism, where males and females have dramatically different appearances. Males are dark and carry impressive spiraled horns and a noticeable mane, while females are lighter in color with distinctive white lateral stripes and no horns. This contrast is more pronounced in Nyalas than in most other antelope species, making them unique in the African wildlife landscape.
Where can I see Nyalas in the wild?
Nyalas are native to Southern Africa and can be observed in countries like South Africa, Mozambique, Malawi, and Zimbabwe. They are often found in protected areas such as national parks and game reserves where their natural habitats of dense woodland and thickets are preserved. Kruger National Park in South Africa and Gorongosa National Park in Mozambique are among the prime locations for Nyala sightings.
Are Nyalas endangered?
As of the last assessment, Nyalas are not classified as endangered. However, they do face threats from habitat destruction due to human expansion, deforestation, and agriculture, as well as from poaching in certain regions. Their populations are relatively stable in well-protected areas but are vulnerable where conservation measures are lax. Ongoing efforts are essential to maintain their numbers and protect their natural habitats.
How do Nyalas contribute to their ecosystem?
Nyalas play a significant role in their ecosystem as browsers, feeding on a variety of foliage, fruits, and flowers. This diet helps to control vegetation growth, ensuring a balanced ecosystem. Additionally, as prey animals, they are integral to the food chain, supporting populations of predators like lions, leopards, and wild dogs. Their presence indicates a healthy, functioning ecosystem and contributes to biodiversity.
What are the main challenges facing Nyala conservation?
The main challenges facing Nyala conservation include habitat loss and fragmentation due to increasing agriculture, human settlement expansion, deforestation, and poaching. Such pressures not only reduce the available habitat for Nyalas but also limit their access to essential resources like food and water, making survival more difficult. Effective conservation strategies must address these issues by protecting habitats, enforcing anti-poaching laws, and promoting sustainable land-use practices.
Can Nyalas be found in captivity?
Yes, Nyalas can be found in captivity, including zoos and wildlife parks around the world. While they can thrive in such environments if given appropriate care and space, these settings cannot fully replicate their natural habitats. Captive breeding programs can play a role in education and conservation by raising awareness about Nyalas and contributing to genetic diversity, but the ultimate goal is to support healthy, wild populations in their natural environments.
How can I contribute to the conservation of Nyalas and their habitat?
Contributing to the conservation of Nyalas and their habitat can take many forms. Supporting and visiting national parks and game reserves that protect these creatures helps generate revenue for conservation efforts. Donating to wildlife conservation organizations working in Southern Africa directly contributes financial resources needed to combat poaching and habitat loss. Additionally, raising awareness about the importance of Nyalas and the threats they face through social media and community engagement can help garner wider support for conservation initiatives.
What makes Nyala sightings a unique experience for wildlife enthusiasts?
Nyala sightings provide a unique experience due to the animals’ elusive nature and stunning appearance. Observing the contrasting colors and behaviors of the male and female Nyala in their natural habitat offers an unparalleled opportunity to appreciate the diversity and complexity of African wildlife. Their preference for dense bush and forested areas makes sightings challenging yet rewarding, capturing the essence of a true wilderness adventure.
What research is being done on Nyala behaviors and population dynamics?
Research on Nyala behaviors and population dynamics focuses on understanding their social structure, reproductive habits, feeding preferences, and migration patterns. This research is crucial for informing conservation strategies, as it provides insights into how Nyalas interact with their environment and with other species. Studies often involve tracking individuals using GPS collars, monitoring herds within reserves, and analyzing genetic diversity to ensure healthy populations.
How do community-based conservation strategies benefit Nyalas?
Community-based conservation strategies involve local populations in the preservation and management of natural resources, creating a sustainable coexistence between humans and wildlife. For Nyalas, these strategies can include habitat restoration projects, anti-poaching patrols, and educational programs about the importance of biodiversity. By involving communities in these efforts, conservation becomes a shared responsibility, leading to more effective protection of Nyalas and their habitats, and ultimately fostering a culture of conservation.