The Significance of Hajj in Islamic Tradition
The Significance of Hajj in Islamic Tradition
Hajj, the annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, holds profound religious importance for Muslims worldwide, symbolizing unity, spirituality, and the fulfillment of one of the pillars of Islam. As the fifth pillar, it is a mandatory religious duty for Muslims who are physically and financially capable of undertaking the journey at least once in their lifetime. The rituals of Hajj are performed annually in the twelfth month of the Islamic lunar calendar, Dhul-Hijjah, and culminate in a deeply spiritual experience that seeks to renew faith, seek forgiveness, and symbolize the equality of all believers in the eyes of Allah.
The Historical Foundations of Hajj
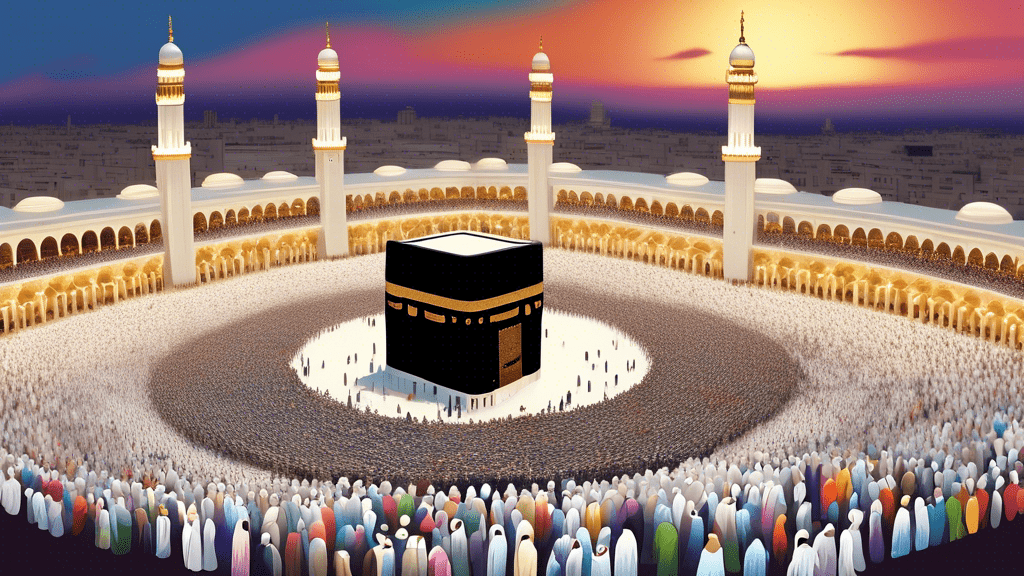
The roots of Hajj can be traced back to the time of Prophet Ibrahim (Abraham) and his family, whose acts of devotion and submission to Allah’s will are commemorated through the pilgrimage’s rituals. According to Islamic tradition, the Kaaba, the cube-shaped structure towards which Muslims around the world turn in prayer, was originally built by Ibrahim and his son Ismail (Ishmael) as a monument dedicated to the worship of the one true God. The inclusion of other rites, such as the Sa’i (running between the hills of Safa and Marwah), and the stoning of the pillars (symbolizing the rejection of temptation), further reflect historical events associated with Ibrahim’s life, particularly his and Hagar’s (Hajar’s) trust in God’s provision and protection.
Unity and Equality Among Pilgrims
One of the most visually striking aspects of Hajj is the sight of millions of believers, dressed in simple white garments (Ihram), performing the rituals together, regardless of their nationality, race, or social status. This uniformity serves not only as a symbol of purity and humility before God but also as a powerful reminder of the equality of all humans in Islam. The universal nature of Hajj fosters a sense of brotherhood and solidarity, making it a unifying experience for the global Muslim community, Ummah, transcending geographical and cultural boundaries.
Spiritual Renewal and Forgiveness
The journey to Mecca is as much an inward journey as it is a physical one. Pilgrims enter into a state of Ihram, which not only consists of wearing specific garments but also entails a spiritual purification and the intention to perform Hajj. The practices involved, such as circulating the Kaaba (Tawaf), standing at Arafat in contemplation and prayer, and partaking in rituals that echo the trials of faith faced by Ibrahim and his family, are designed to strip away the distractions of worldly life, focusing the heart and soul on devotion to Allah. The climax of Hajj at the Mount of Mercy (Arafat) represents an opportunity for direct communion with God, where pilgrims seek forgiveness for their sins. It is believed that those who perform the Hajj with sincere faith and repentance return as sinless as a newborn.
Conclusion
The significance of Hajj in Islamic tradition cannot be overstated. It stands as a testament to faith, a journey of spiritual cleansing, and an expression of the collective identity of Muslims around the world. Beyond its religious obligations, Hajj serves as a source of inspiration and aspiration for millions, reminding them of the universal values of brotherhood, equality, and the eternal pursuit of divine closeness. As one of the largest religious gatherings on Earth, it continues to foster a global sense of community and shared purpose among Muslims, echoing the timeless message of unity and faith.
FAQs about Hajj
Why is Hajj considered a pillar of Islam?
Hajj is considered one of the five pillars of Islam, which are foundational acts of worship that define a Muslim’s faith and practice. It is obligatory for all Muslims who are physically and financially able to undertake it at least once in their lifetime. This obligation is rooted in the Quran, where Allah commands Muslims to perform Hajj to the Kaaba if they have the means to do so. As such, it represents a key component of Islamic devotion, emphasizing the importance of submission to Allah, demonstrating unity among the Muslim Ummah, and fulfilling a lifelong aspiration for many believers.
What are the main rituals performed during Hajj?
There are several key rituals that constitute the Hajj pilgrimage, each with deep spiritual meaning and historical significance. These include entering a state of Ihram, where pilgrims wear simple white garments and observe various prohibitions; performing Tawaf, which is the circumambulation of the Kaaba; the Sa’i, walking between the hills of Safa and Marwah; standing in prayer at Arafat; spending a night in the plain of Muzdalifah; participating in the stoning of the pillars at Mina; and finally, the symbolic act of sacrificing an animal in remembrance of Ibrahim’s willingness to sacrifice his son in obedience to God’s command. Collectively, these rituals reenact the faith and dedication of Ibrahim and Ismail, reinforce the commitment to Islam, and signify submission to Allah.
How does Hajj promote unity and equality?
Hajj promotes unity and equality among Muslims by bringing together followers of Islam from all corners of the globe, regardless of nationality, race, or socioeconomic status, to perform the same acts of worship at the same time and location. The wearing of Ihram, the white garments, is a powerful equalizer, stripping away external indicators of wealth, power, and prestige, and highlighting the common humanity and vulnerability of all pilgrims. This shared experience fosters a sense of belonging to a global community, the Ummah, and emphasizes the core Islamic values of brotherhood, solidarity, and social equality.
Can anyone perform Hajj, or are there specific requirements?
To perform Hajj, there are specific requirements that must be met, emphasizing its importance as a significant commitment and act of worship in a Muslim’s life. First and foremost, the individual must be a Muslim. Secondly, they must be of sound mind and physically able, which includes having the physical stamina to complete the rituals and being free from any ailments that would make the journey intolerably difficult. Financial ability is also crucial, as the pilgrim must be able to afford the trip without causing hardship to themselves or their dependents. Additionally, for women, it is required to have a mahram (a male relative whom they cannot marry) accompany them, if they are not traveling with a husband or family group. These requirements ensure that the act of performing Hajj is both a feasible and meaningful endeavor for those who undertake it.
What is the spiritual significance of standing at Arafat during Hajj?
The standing at Arafat, known as the Day of Arafah, is considered the climax and an essential rite of the Hajj pilgrimage, holding immense spiritual significance. It commemorates the day when Prophet Muhammad delivered his Farewell Sermon, emphasizing the core tenets of Islam. This part of the pilgrimage is an opportunity for deep reflection and supplication, where pilgrims stand in the plain of Arafat, asking for Allah’s forgiveness and mercy. It is believed that on this day, Allah descends to the nearest heaven and proudly tells the angels of the forgiveness granted to the throngs of repentant pilgrims gathered. The spiritual renewal experienced at Arafat symbolizes a rebirth; pilgrims who sincerely seek forgiveness are said to be cleansed of their sins, returning as pure as the day they were born.
How has modern technology impacted the Hajj experience?
Modern technology has significantly impacted the Hajj experience, making it more accessible and safer for pilgrims. Innovations such as electronic visa processing, online registration for the Hajj, and mobile apps for navigation and translation services have streamlined preparations and logistics. The Saudi government and various tech companies have also introduced apps and services to help pilgrims with everything from travel arrangements to performing the rites correctly. Moreover, health and safety technologies, including crowd control mechanisms, GPS tracking bracelets, and enhanced medical services, have improved the overall safety and comfort of the pilgrimage. While technology has modernized the Hajj experience, the spiritual and communal essence of the pilgrimage remains unchanged.
What are the environmental and health challenges associated with Hajj?
The Hajj pilgrimage presents several environmental and health challenges, largely due to the vast number of people it attracts each year, which can exceed two million. Environmental issues include considerable waste generation, water consumption, and air pollution, all of which pose significant challenges to sustainability efforts in the region. On the health front, the high density of pilgrims in close quarters increases the risk of communicable diseases, such as respiratory infections, heat-related illnesses, and, in past years, outbreaks of meningitis and the MERS virus. To address these concerns, the Saudi authorities have implemented extensive health and safety measures, including vaccination requirements, health screening at entry points, and a considerable presence of medical personnel and facilities throughout the pilgrimage sites. Additionally, sustainability initiatives aimed at waste management, water conservation, and green transportation options are increasingly becoming a focus to mitigate environmental impacts.
Can non-Muslims participate in or observe Hajj?
Non-Muslims are not permitted to participate in or physically observe Hajj within the holy sites of Mecca and Medina. The Islamic tradition reserves this spiritual journey strictly for Muslims, as it entails performing rituals that signify the deep aspects of Islamic faith and devotion to Allah. The exclusion is not meant as a form of discrimination but as a protection of the sanctity and religious focus of the pilgrimage. However, non-Muslims are welcome to learn about Hajj through various other channels, such as documentaries, books, and lectures, and many Muslims are eager to share their experiences and the significance of Hajj with interested parties from different faiths and backgrounds.
What is the impact of Hajj on a pilgrim’s life after returning home?
The impact of Hajj on a pilgrim’s life after returning home can be transformative, affecting spiritual, social, and personal dimensions of their life. Spiritually, successfully completing Hajj often leads to a renewed sense of faith and a deeper commitment to Islamic practices and values. Socially, pilgrims return with a strengthened sense of unity and brotherhood with Muslims from diverse backgrounds and cultures, having shared in one of Islam’s most profound communal experiences. Personally, the journey can also lead to increased discipline, humility, and gratitude, reflecting the transformative potential of this profound act of worship. Many pilgrims report a lasting influence on their perspective towards life, priorities, and relationships, striving to live with greater purpose and closeness to their faith.
What are the challenges pilgrims face during Hajj, and how do they prepare?
Pilgrims face various challenges during Hajj, ranging from physical and logistical to spiritual. Physically, the demands of performing the pilgrimage rituals, often in extreme heat and amidst large crowds, can be strenuous. Logistically, navigating the requirements for travel, accommodation, and understanding the intricacies of the rituals can be complex, particularly for those from distant lands. Spiritually, preparing one’s heart and mind for the profound religious experience of Hajj is a significant endeavor. Pilgrims prepare by saving financially for the trip, attending Hajj preparation classes to learn the rituals and their meanings, and engaging in spiritual practices such as prayer and fasting to ready their hearts for the journey. Physical preparation, such as walking regularly to build stamina, is also common among prospective pilgrims. This multifaceted preparation is crucial for fulfilling the obligations of Hajj and deriving the deep spiritual benefits it offers.